Unlocking Success: Discover the Ideal 3D Printer for Your Small Business Today!
In today’s rapidly evolving marketplace, small businesses are increasingly turning to 3D printing technology to gain a competitive edge. The ability to create customized products on-demand not only enhances innovation but also significantly reduces costs and lead times. Imagine being able to prototype new designs in a matter of hours rather than weeks, or producing small batches of unique items tailored to customer specifications. This transformative technology empowers small business owners to think creatively and push the boundaries of traditional manufacturing. However, with numerous options available, selecting the right 3D printer can be daunting. This article aims to guide you through the essential features to consider when choosing a 3D printer that aligns with your business needs, ultimately helping you unlock the potential of 3D printing for small businesses for your small enterprise.
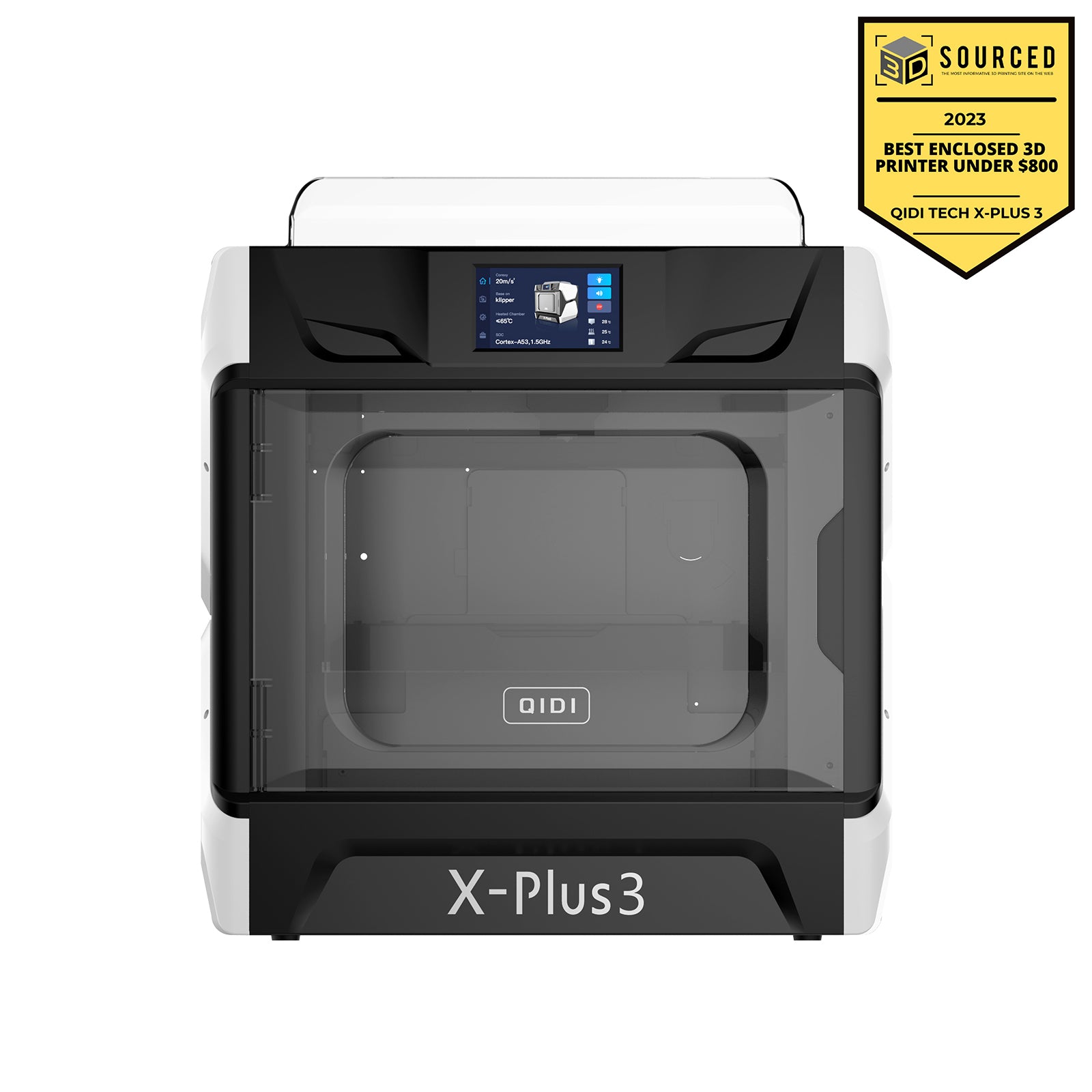

Understanding the Needs of Small Businesses
Small businesses often face unique challenges that dictate their 3D printing needs. One of the primary considerations is production volume. Unlike larger corporations that may require high-volume production runs, small businesses typically operate on a smaller scale, which means they need a printer that can handle short runs efficiently. Additionally, material versatility is crucial; businesses often require a variety of materials—from plastics to metals—to meet diverse customer demands. Furthermore, ease of use is paramount; many small business owners may not have extensive technical expertise, so a user-friendly printer can streamline the learning process. Maintenance is another critical factor; downtime due to printer issues can disrupt operations, so a reliable machine with accessible support is essential. By understanding these unique needs, small businesses can better assess which 3D printer will serve them best.
Key Features to Look for in a 3D Printer
When evaluating 3D printers for small business applications, several key features should be prioritized. First, build size is an essential consideration; the printer should be capable of producing the dimensions required for your projects without the need for extensive assembly. Printing speed is equally important, especially for businesses that operate on tight deadlines. A faster printer can significantly enhance productivity and meet customer demands more effectively. Resolution is another critical factor; high-resolution printers produce finer details and smoother surfaces, which can be essential for certain applications. Finally, connectivity options, such as USB, Wi-Fi, or cloud-based printing, can facilitate easier integration into existing workflows. These features collectively contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of 3D printing in a small business environment.
Types of 3D Printers Suitable for Small Businesses
There are several types of 3D printers, each with its advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different small business applications. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers are the most common and are known for their affordability and ease of use, making them ideal for beginners. However, they may not provide the level of detail required for intricate designs. Stereolithography (SLA) printers, on the other hand, use resin to create highly detailed models but can be more expensive and require more maintenance. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) printers are excellent for industrial applications, offering the ability to print with a wide range of materials, but they typically come with a higher price tag. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these types can help small businesses choose the right technology for their specific needs, whether it's for prototyping, product development, or custom orders.
Best Practices for Implementing 3D Printing in a Small Business
Successfully integrating 3D printing into a small business requires careful planning and consideration. One of the first steps is ensuring that staff members are adequately trained to operate and troubleshoot the printer effectively. This can involve offering hands-on training sessions or providing access to online resources and tutorials. Additionally, managing production workflows is crucial; businesses should develop a clear process for how 3D printing fits into their overall production strategy, whether it's for prototyping or producing final products. Finally, leveraging 3D printing for marketing purposes can significantly enhance a business's visibility. Creating unique promotional items or prototypes for client presentations can showcase the innovative capabilities of the business. By following these best practices, small businesses can maximize the benefits of 3D printing and drive growth.
Maximizing 3D Printing Benefits for Your Business
In conclusion, the right 3D printer can be a game-changer for small businesses, offering unprecedented levels of customization, efficiency, and innovation. By understanding the unique needs of your business, identifying key features, and exploring suitable printer types, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your operational goals. The integration of 3D printing technology can not only streamline production processes but also open new avenues for creativity and customer engagement. As you evaluate potential options, consider how 3D printing can enhance your business's capabilities and drive you toward future success.