When it comes to storage, 3D printing filament requires special accommodation. Among the most popular filament materials of PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU, the most demanding storage requirement would have to be humidity (or lack thereof). After that, the absence of dust and particulates is another important consideration for filament storage.
But of course, you also want your storage to be convenient. Easily accessible filament and an aesthetically pleasing display might be just as important to you as protecting your filament from moisture.
In this article, we’ll take you through some important considerations when planning how to store your filament, then go through the major options to help you find the right solution for your setup. Let’s take a deeper look!
What's the Big Deal?
The majority of materials used in FDM 3D printing can be considered hygroscopic, meaning that they absorb water molecules rather than repel them. This doesn’t mean that your Benchy will act like a sponge, but if you let your filament sit out in the open air, your print quality will go down. Even what we might consider relatively low ambient humidity can be detrimental to filament over time.
Keeping filament in an airtight container is a must to prevent the absorption of water from the air, and using vacuum-sealed containers or ones with desiccant is even better. We’ll go into more detail about desiccants in a moment, but first, let’s look at the warning signs.
Knowing if Your Filament Is Wet
With “wet” filament, you might notice print surface quality getting worse or that you are struggling with layer adhesion. One way to tell if filament is too wet is to listen for popping or crackling sounds when it’s being melted in the hot end. What you’re hearing is the sound of moisture pockets within the filament rupturing and evaporating.
That said, wet filament isn’t a lost cause, as most filaments can be dried using a repurposed food dehydrator, a low-temperature oven, or a purpose-built machine such as some of the ones included at the end of this list.
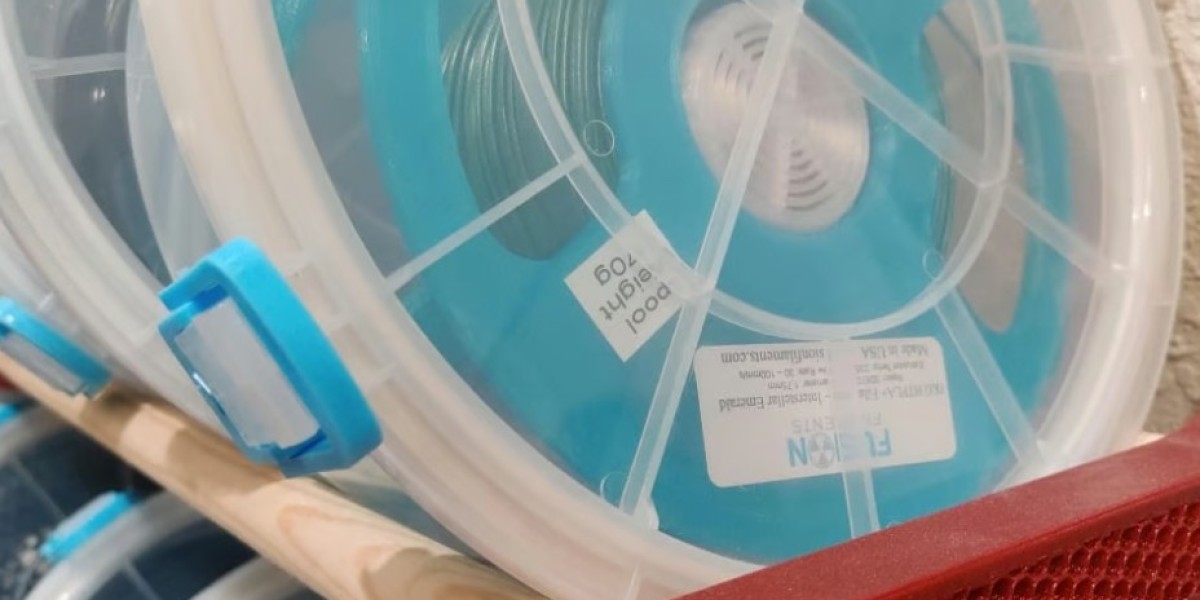
Dry Boxes
A step up from storing your filament on a rack or in bags is a purpose-built dry box. Dry boxes are a long-term storage solution that generally use desiccant in a sealed box to keep your filament in a dry atmosphere.
There are a few DIY options around, including the well-known Prusa Drybox and a 3D printed upgrade for a Rubbermaid container. Those looking for more storage might be interested in a simple solution like a repurposed rolling bin. Or for something a bit more high-tech, electric dry cabinets provide a humidity-controlled environment and come in a range of sizes. These units are more commonly used for the storage of moisture-sensitive items like photography equipment, but why not your filament collection?
If you’d rather buy something designed specifically for protecting your filament, there are a few options.
Dryers
If you have a wet spool of filament, a dry box or bag with desiccant can’t really get rid of the moisture. These solutions are only designed to prevent any more moisture from reaching the filament. That’s where dedicated filament dryers come in.
Most filament dryers work by storing filament in a gently heated environment to evaporate any moisture. Purchasable dryers often offer extra features, too, like a timer, display, temperature controller, or fan. Just keep an eye on your power bill, as an electrical device might prove an expensive way to store your filament in the long term.