Unlocking the Secrets: Why PETG and PLA Filaments Could Transform Your 3D Printing Game!
3D printing has revolutionized the way we create and innovate, allowing hobbyists and professionals alike to bring their ideas to life. One of the most crucial decisions in this process is selecting the right filament, as it can significantly impact the quality and durability of your prints. Among the various options available, PETG and PLA filaments stand out as popular choices for different reasons. PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, is known for its strength and flexibility, making it ideal for functional parts. On the other hand, PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is favored for its ease of use and eco-friendliness. In this article, we'll dive deeper into the differences between these two materials, helping you make an informed choice for your 3D printing projects.
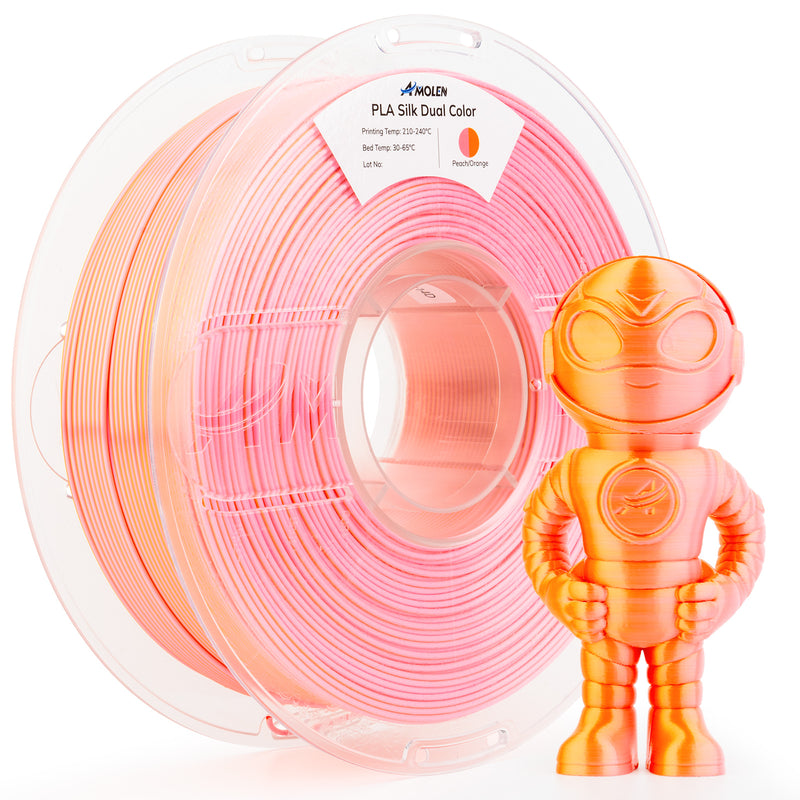

Understanding PETG and PLA Filaments
To fully grasp the nuances of PETG and PLA, it’s essential to understand their chemical compositions and properties. PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic made from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, which makes it an eco-friendly option. It is known for its low melting temperature, which allows for easier printing and produces excellent detail and finish. However, this lower temperature also means PLA can be more brittle and less durable in high-stress applications. Conversely, PETG is a modified version of PET (the plastic commonly used in water bottles), enhanced with glycol to improve its clarity and impact resistance. This filament offers a combination of the best features of both ABS and PLA, boasting excellent chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility. Both materials have unique characteristics that cater to different printing needs, making it crucial to choose wisely based on your project requirements.
Comparing Advantages of PETG and PLA
When it comes to advantages, both PETG and PLA have their unique strengths. PLA is often praised for its ease of use, making it an excellent choice for beginners. It adheres well to the print bed and typically does not require a heated bed, which simplifies the printing process. Additionally, PLA produces smooth prints with high detail due to its low shrinkage and warping characteristics. My friend, who recently took up 3D printing, found that PLA was perfect for his intricate models, as he could achieve stunning results without much hassle. On the other hand, PETG excels in applications requiring strength and durability. It has a higher impact resistance than PLA, making it ideal for functional parts, mechanical assemblies, and outdoor applications. PETG also has excellent layer adhesion, leading to stronger prints that can withstand stress. If you’re printing items that will be subjected to wear and tear, PETG might be the better choice.
Examining Disadvantages of PETG and PLA
While both PETG and PLA have their merits, they also come with disadvantages that can affect your 3D printing experience. PLA, despite its ease of use, can be less suitable for high-temperature environments. It tends to soften at temperatures above 60°C, which may lead to deformation in applications requiring heat resistance. Additionally, although PLA is biodegradable, it requires specific conditions to break down effectively, rendering it less environmentally friendly in some situations. On the other hand, PETG can pose challenges during printing. It has a higher tendency to string and can require more tuning to achieve optimal results. Warping is less of a concern with PETG than with other materials, but it can still occur if not printed correctly. Moreover, the need for a heated bed can be a drawback for those using lower-end printers. Understanding these disadvantages will help you navigate the potential pitfalls of each filament and make adjustments as needed.
Practical Applications: When to Use Each Filament
Choosing the right filament often depends on the specific requirements of your project. For decorative items and prototypes where detail is paramount, PLA is a fantastic option. Its vibrant colors and smooth finish make it ideal for visual applications such as figurines, art pieces, or educational models. I remember when my friend printed a complex architectural model using PLA; the results were stunning, showcasing intricate details that would have been lost with other materials. Conversely, for functional parts like mechanical components, brackets, or even outdoor items that need to withstand the elements, PETG is the better choice. Its durability and resistance to moisture make it well-suited for projects exposed to varying conditions. Additionally, PETG’s flexibility allows for more complex geometries that may require bending or stress without breaking. Ultimately, assessing the specific needs of your project will guide you in selecting the most appropriate filament.
Final Thoughts on Choosing PETG or PLA
In summary, both PETG and PLA filaments offer unique benefits and drawbacks that cater to different 3D printing needs. PLA stands out for its ease of use and excellent surface finish, making it a great choice for beginners and aesthetic projects. However, it may fall short in high-temperature applications. Meanwhile, PETG impresses with its durability and versatility, making it suitable for functional and outdoor applications, though it may require more careful handling during printing. When embarking on your 3D printing journey, consider your specific project requirements and preferences. Making an informed choice between PETG and PLA can significantly enhance your printing experience and the quality of your final products.